Choose Your Child's Gender Through Advanced IVF Genetic Screening
In many countries, genetic screening before embryo transfer is standard practice in IVF procedures. However, regulations regarding gender selection vary.
%20(1080%20x%201080%20%E5%83%8F%E7%B4%A0)%20(10).png)
Regulations
For example, in the UK, clinics perform Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) to assess embryo viability and genetic health, but they do not disclose the gender of the embryos to intended parents. Additionally, the UK has strict regulations on the import and export of embryos.
In contrast, in the US, gender selection is legally permissible in IVF procedures. Intended parents have the option to choose the gender of their embryos, and clinics offer this service as part of the IVF process.
Embryo Creation

Egg Retrieval and Fertilization
The eggs will be fertilized in the lab
The Cells will Multiply



Over 120 Cells will be Created in 5-7 Days

Embryo Freezing
The Fertilized Eggs Will Split
After the biopsy, the sample will be tested for chromosomal abnormalities. The embryos will then be frozen and stored in the lab.
What is PGT testing for?
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) is an advanced technique in assisted reproduction that checks embryos for genetic abnormalities before implantation. It helps identify conditions like Down syndrome and cystic fibrosis, ensuring healthier embryos are selected for IVF. By detecting potential issues early, PGT improves IVF success rates and reduces the risk of inherited disorders, offering hope to couples undergoing fertility treatment.
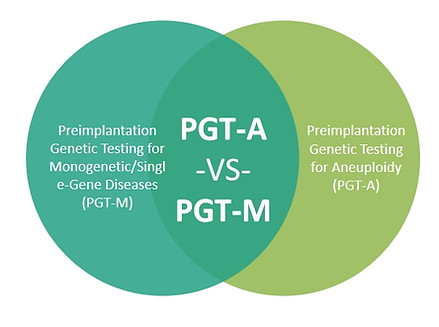
What is the Difference?
Both PGT-A and PGT-M involve taking a small sample from embryos, usually at the blastocyst stage (around 5-6 days after fertilization). PGT-A checks the overall chromosome count to make sure the embryos have the right number of chromosomes, which is important for a healthy pregnancy. PGT-M, on the other hand, looks for specific genetic mutations linked to inherited disorders, helping to identify embryos that might be at risk for these conditions.

Understanding Genetic Screening
01
PGS → PGT-A
Gender selection can aid in preventing the inheritance of specific genetic diseases, such as Cystic Fibrosis, Tay Sachs, Huntington’s disease, or sickle cell disease, which are carried on the X or Y chromosome.
However, it's important to note that Microsort does not currently offer this service.
02
Gender Selection
Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS) assesses embryos for the correct number of chromosomes, which are essential for proper development and function. Chromosomes, like an instruction manual, contain vital DNA information. Missing or extra chromosomes can lead to health issues. PGS identifies these abnormalities, boosting the chances of successful pregnancies and reducing the risk of genetic disorders.
03
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) is crucial for individuals concerned about passing genetic diseases to their children. During IVF, PGD screens embryos for specific genetic conditions, ensuring only healthy embryos are selected for implantation.
Our expert team analyzes embryos' genetic makeup to identify potential abnormalities, offering vital information for informed decisions. PGD can detect a range of genetic disorders, including:
-
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
-
Tay Sachs Disease
-
Hemophilia A and B
-
Sickle Cell Anemia
-
Gaucher’s Disease
By analyzing embryos for these common chromosomal issues, PGD helps identify those most likely to result in a healthy pregnancy. For couples experiencing unexplained IVF failures, PGD may also reveal potential causes.
The PGT Process:


_edited.png)